Process for Co-sintering Additive Manufacturing Parts
Case ID:
TEC2023-0017
Web Published:
7/1/2024


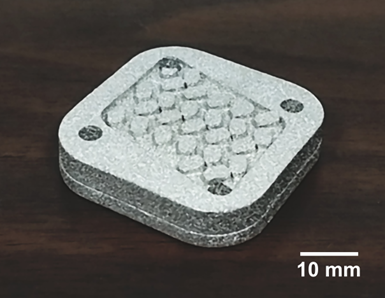
FABRICATED GREEN HEAT EXCHANGER PLATES BY SEAM PROCESS SINTERED STACKED HEAT EXCHANGER ASSEMBLY
Executive Summary
Metal additive manufacturing is an attractive process for producing highly complex and tailored components from superalloys for high temperature applications. However, the processes can be slow and are not scaleable for large volume production. Researchers at Michigan State University have recently developed an efficient additive manufacturing process for metal parts that is scalable, low cost and creates parts with very high relative densities with no geometrical distortion. The process can be also used to make complex structures with enclosed channels.
Description of the Technology
The technology is based on an additive manufacturing process using UV light curing of mixture composed of a photopolymer and metal powders. This process termed SEAM (scalable and expeditious additive manufacturing) involves a curing mechanism and co-debinding and co-sintering of multiple parts. Experiments have been conducted using a Haynes 214, Nickel based superalloy to manufacture parts for a high temperature super critical CO2 heat exchanger.
Benefits
- Scalable manufacturing process allows multiple parts to be formed at the same time
- Design simplicity
- Cost effective process reduces manufacturing time
- Allows production of parts with enclosed channels and complex internal structures
- Can co-debind and co-sinter multiple green parts together in a single heating cycle
- High part density achieved up to 99.5% relative density with no geometrical distortion
- Homogenous microstructure parts with low residual stress which does not need any additional heating cycles
- Superior surface roughness compared to laser sintered process
Applications
- Parts for high temperature applications including engine turbine blades, nuclear reactors, turbochargers, heat exchangers
- Automotive parts
- Medical / Dental parts and devices
- End of arm tooling
- Jewelry
Patent Status
Licensing Rights
Full licensing rights available
References
“From Photopolymerization of Metal Suspension to Practical and Economical Additive Manufacturing of Haynes 214 Alloy for High Temperature Application”, International Additive Manufacturing Conference IAM2022, 10/19/22
"Photopolymerization of Stainless Steel 420 Metal Suspension: Printing System and Process Development of Additive Manufacturing Technology toward High-Volume Production", Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2024
Inventors
Dr. Haseung Chung, Dr. Patrick Kwon
TECH ID
TEC2023-0017
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |
For Information, Contact:
Jon Debling
Technology Manager
Michigan State University
deblingj@msu.edu