Executive Summary
Fasteners are often installed through holes drilled in individual pieces to be joined. While significant advancements have been made in fasteners over the past several decades, construction techniques such as using composites (including wood, fiberglass, and carbon fiber), in particular, have exposed serious limitations to existing fastener capabilities. Advanced fasteners are often required for dissimilar and advanced materials, especially modern composite structures. Michigan State University has developed a hybrid fastening system with an associated installation process that involves a standard fastener type coupled with a liquid or elastomeric insert filler material. The fastener is easy to install with high tolerance for misaligned holes and provides reliable sealing against moisture and contamination and durable joint performance.
Description of the Technology
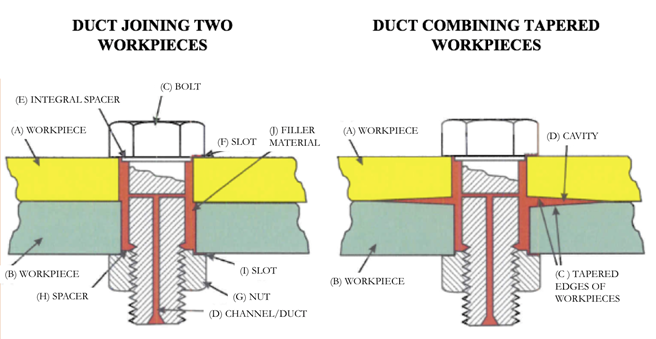
The invention involves a standard fastener type coupled with a liquid or elastomeric insert filler material. To use the system, the fastener is installed in much the same fashion as a normal fastener and serves a similar function, with an axial load applied to ensure adequate shear strength. In addition, however, a filler material (such as polyurethane, silicone, or epoxy) is added to the joint to help seal out moisture and debris contamination and lower contact stresses, yielding better fatigue performance. Conceptually, the filler material is installed either through direct injection, or through a capsule that is installed within the joint and which opens and allows the filler to flow into the joint as the fastener is secured.
Benefits
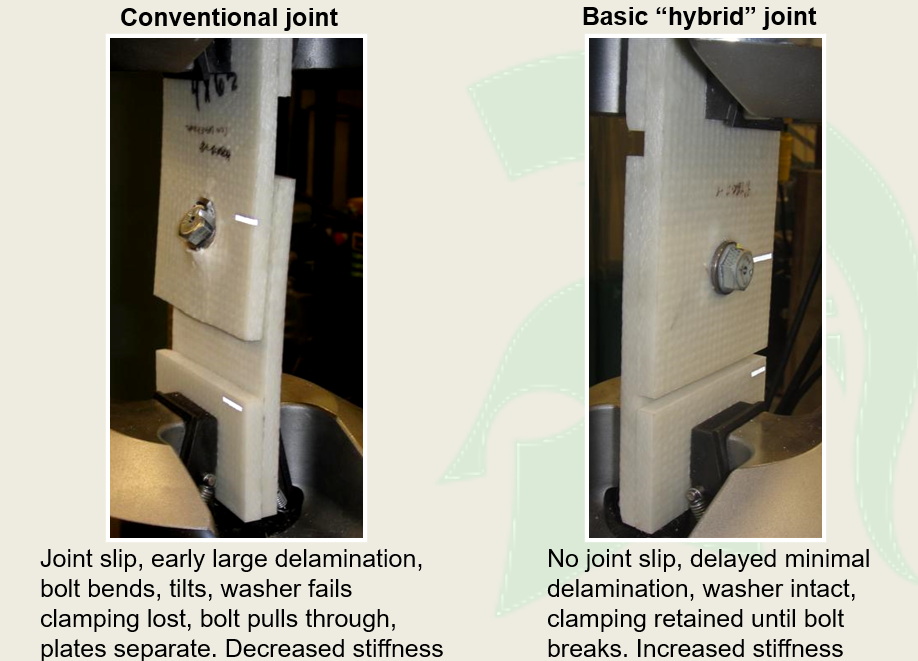
- Higher joint strength: Exhibits the combined benefits of fastener, insert, and adhesive patch elements.
- Increased fatigue performance: The lower contact stresses and filled joint helps prevent contaminant entry.
- Less sensitivity to misaligned work pieces: The filler adjusts misalignment voids.
- Better sealing against moisture and debris contamination: The filler provides a complete joint seal that is challenging when fastening composite materials.
- Less dependence on precision-drilled work piece holes.
Applications
- Composite Structures
- Transportation
- Aerospace
- Defense
- Wind Turbines
- Building construction
- Marine
Patent Status
Issued patents, US 9,464,658 and US 10,400,813
Licensing Rights
Full licensing rights available
References
"Fastener inserts and hybrid joining for composites and other materials", W.M. Murray Lecture, SEM XII International Congress, 2012
"Novel Hybrid Fastening System with Nano-additive Reinforced Adhesive Inserts", Conference: 2014 SEM Conference & Exposition on Experimental & Applied Mechanics, 2015
"Fatigue Behavior of Novel Hybrid Fastening System with Adhesive Inserts", Conference proceedings, Fracture, Fatigue, Failure and Damage Evolution, 2016
Inventors
Dr. Gary Cloud
TECH ID
TEC2010-0057